Anexos:
FOTO: 1. TAC de cráneo evidenciando lesión.
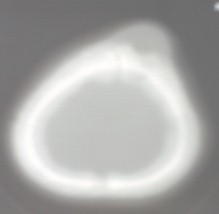
FOTO: 2. TAC de cráneo lesión lítica expansiva en hueso frontal.
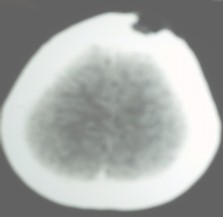
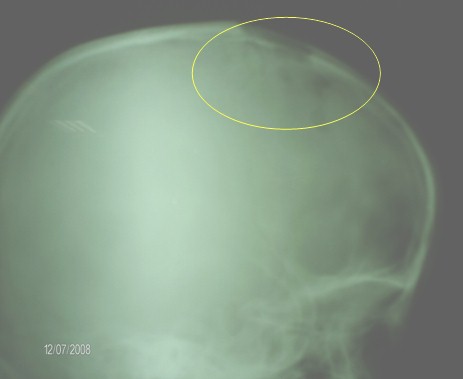
FOTO: 3. Rx de cráneo- lesiones osteolíticas.
Referencias bibliográficas
1. Akhtar M, Ali MA, Bakry M, Sackey K, Sabbah R. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of Langerhans histiocytosis (histiocytosis-X). Diagn Cytopathol 1993; 9(5):527-533.
2. Brooder G, Maris J. Neuroblastoma. En: Pizzo P, Poplack D, editores. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002: 895-937.
3. Bucks P, Egeler RM. Malignant histiocytic disorders in children. Clinical and therapeutic approaches with a nosologic discussion. Hematol Oncoi Clin North Am 1998; 12(2):465- 47l.
4. Egeler RM, Favara BE, van MM, Laman JD, Claassen E. Differential Insitu cytokine profiles of Langerhanslike cells and T cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis: abundant expression of cytokines relevant to disease and treatment. Blood 1999; 94(12): 4195- 4201.
5. Favara BE, Feller AC, Pauli M et al. Contemporary classification of histiocytic disorders. The WHO Committee On Histiocytic/Reticulum Cell Proliferations. Reclassification Working Group of the Histiocyte Society. Med Pediatr Oncol 1997; 29(3):157-166.
6. Gadner H, Grois N, Arico M et al. A randomized trial of treatment for multisystem Langerhans’ cell histiocytosis. J Pediatr 2001; 138(5).
7. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2002: 733-750.
8. Larroche C, Mouthon L. Pathogenesis of hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS). Autoimmun Rey 2004; 3(2):69-75.
9. Mitomi T, Tomizawa M, Noda T. Tooth devehopment included in the multifocal jaw lesions of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Int j Pediatr Dent 2005; 15(2): 123-126.
10. Sandlund JT, Downing JR, Crist WM. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in childhood. N Engl J Med 1996; 334(19):1238-1248.