Presentacion de caso clinico. Aneurisma cerebral roto paciente con enfermedad renal poliquistica .3
Figura # 5. Hemorragia Subaracnoidea e Intraventricular Nivel Líquido – Líquido.
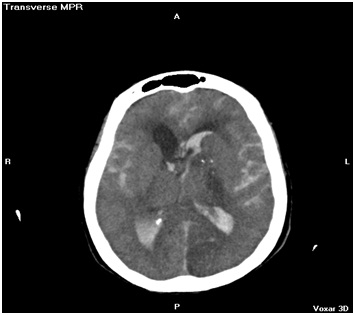
Figura # 6. Reconstrucción multiplanar (MPR) 3D del mismo paciente.
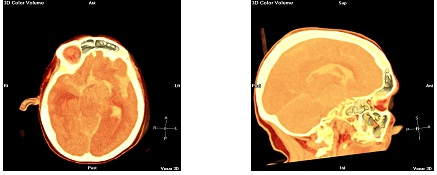
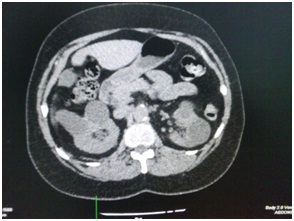
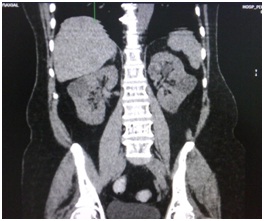
Figura # 7. TAC abdominal simple que muestra en cortes axial y coronal la presencia de quistes renales bilaterales.
Bibliografía:
1. Waugh JR, Scharias N: Angiographic complications in the DSA era. Radiology 182: 243–246,
2. Hope JKA, Wilson JL, Thompson FJ. Three dimensional CT angiography in the detection and characterization of berry aneurysms. Am J. Neuroradiol. 17: 439 – 445, 1996.
3. Houston J III, Torres V W, Sullivan PP, et al. Value of magnetic resonance angiography for the detection of intracranial aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic Kidney disease. J. Am Soc. Nephrol. 3: 1871–1877, 1993.
4. Inagawa, T. Hirano, A. Autopsy study of unrupture incidental aneurysm. Surg. Neurol. (30): 361 – 365, 1990.
5. Juvela, S., Hillborn, M., Numminen, H. et al. Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption as risk factors for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 639-646, 1993.
6. Kassel NF, Torner JC, Jane JA, et al: The International Cooperative Study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. Part l: Overall management results. J. Neurosurg. 18–36, 1990.
7. Heiserman JE, Dean BL, Hodak JA et al: Neurologic complication of cerebral angiography. AJNR 15: 1401–1407, 1998.
8. . King, Joseph T. Jr. Epidemiology of aneurismal subarachnoid hemorrhage; Neuroimaging Clinics of North America 7: 659–668, 1997.
9. Knuckey, N.W., Haas, R, Jenkins, R. et al. Trombosis of difficult intracranial aneurysms by endovascular placement of platinum – Dacron microcoils. J. Neurosurg 77: 43–50, 1992.
10. Kyra Becker. Epidemiology and clinical presentation of aneurysmal subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery Clinics of Norteamérica 9: 435 – 444, 1998.
11. Newell D W, Le Roux PD, Dacey RG Jr. et al: C T infusion for the detection of cerebral aneurysms. J. Neurosurg 71: 175–179, 1989
12. Ogawa T, Okudesa T., Noguchi K, et al. Cerebral Aneurysms: Evaluation with three dimensional C T angiography. Am J. Neuro Radiol 17: 447–454, 2001.
13. Phillips, L. H, Whisnant, J. P., O´Fallow, W.N. et al. The unchanging pattern of subarachnoid hemorrhage in a comunity. Neurology 30: 1034 – 1040, 1980.
14. Rinkel GI., Wijdicks, EF, Hasan, D et al. Autcome in patients with subarachnoid hemorrahage and negative angiography according to pattern of hemorrhage on computed tomography. Lancet 338: 964–968, 1998.
15. Sahs, H. Nibbelink, D. W. and Torner, J. C. (eds) Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Report of the cooperative Study. Urban and Schwarzemberg, Baltimore, 2010.
16. Schiewink, WI. Wijdicks, EFM. Parisi, JE. et al Sudden death from aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 45: 871 – 874, 1995.
17. Suzuki, J. Onuma, T., Yoshimoto, T. Results of early operations on cerebral aneurysms. Surg. Neurol 11: 407-412, 1999.
18. Teunissen, L., Rinkel, G., Algra, A. et al. Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Stroke 27: 544–549, 2007.