|
Sindrome compartimental abdominal .6
Estos problemas se solucionan con el empleo de distintos tipos de prótesis de cobertura, que incluyen desde una media de nylon hasta mallas prediseñadas como mallas absorbibles, mallas de Prolene y mallas de Silastic, con cierta preferencia por la primera, por su bajo costo y amplia disponibilidad. (7, 20. 22) Los materiales mencionados se usan por supuesto también en el tratamiento post descompresión del síndrome compartimental abdominal (SCA) en pacientes que previamente no se les había colocado en el acto operario como medida preventiva. (29, 36, 54, 69)
La figura 4 muestra el efecto de la reintervención sobre la hipertensión intraabdominal.
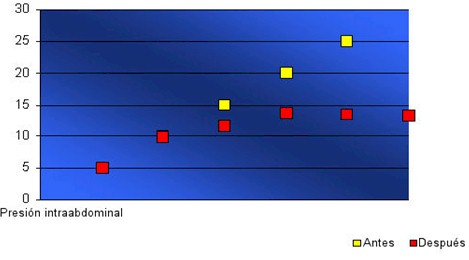
Figura 4: Comportamiento de la presión intraabdominal antes y después de la reintervención. (Tomado de una tesis para la terminación de residencias). (70)
En el Hospital Universitario “Dr. Juan Bruno Zayas Alfonso”, hemos realizado tesis de maestría acerca de la validación de la medición de la presión intraabdominal (a través de sondaje vesical) como índice de predicción de reintervención intraabdominal en pacientes portadores de abdomen agudo, mostrando esta sencilla prueba una sensibilidad y especificidad por encima de 90%. Este preceder es de uso cotidiano en todos los pacientes sometidos a cirugía abdominal ingresados en UTI de nuestro centro.
Referencias Bibliográficas
1. Tollenz T, Janzing H, Broos P. The pathophysiology of the acute Compartment Syndrome. Acta Chir Belg. 1998; 98(4):171-5.
2. Liolios A, Oropello JM, Benjamin E. Gastrointestinal complications in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin Chest Med. 1999; 20(2):329-44.
3. Sieh KM, Kent-Man, Chu John W. Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome. Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery. 2002; 386(1):53-61.
4. Maxwell RA, Fabian TC, Croce MA, Davis KA. Secondary abdominal compartment syndrome: an underappreciated manifestation of severe hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma 2004; 12; 47(6):995-9.
5. Balogh Z, Mckinley, phd, Holcomb MD, et al. Both Primary And Secondary Abdominal Compartment Syndrome (ACS) Can Be Predicted Early And Are Harbingers Of Bad Outcome. Oral Presentation. The American Association for the Surgery of Trauma 2002.
6. Lacey ST, Bruce J. The relative merits of various methods of indirect measurement of intra-abdominal pressure as a guide to closure of abdominal wall defects. J.Pediatric Surg, Dec 1987; 22 (12): 1207-11.
7. Lovesio C. Síndrome compartimental abdominal. Rev Med Rosario 2002; 68:97-100.
8. Hong JJ, Cohn SM, Perez JM, Dolich MO. Prospective study of the incidence and outcome of intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. British Journal of Surgery. 2002; 89 (5), 591.
9. Aragón Palmero F, Curbelo Pérez R, Candelario López R, Hernández Jm. Nuevos conceptos en cirugía: Síndrome del compartimiento abdominal. Rev Cub Cir 2003; 38 (1): 30- 5.
10. Burch Jm, Moore EE, Moore Fa, Françoise R: The abdominal compartment Syndrome. Surg Clin North AM 2004; 76(4): 833- 41.
11. Kas huk Jl, Moore EE, Millican Js, Moore Jb. Major Abdominal Vascular trauma: A unified Approach. J Trauma 1982; 22: 672-9.
12. Emerson H. Intra- abdominal Pressure. Arch intern Med 1911; 7: 754- 84.
13. Morris Ja,et al. The staged Celiotomy for trauma. Ann Surg 2003; 217/ 576- 85.
14. Malbrain, MLNG. Abdominal pressure in the critically ill. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2003; 6: 17-29.
15. Gajic O, Urrutia Le. Acute abdomen in the medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med.2002; 30:1187-90.
16. Mayberry JC, Goldman RK, Mullins RJ. Surveyed opinion of American trauma surgeons on the prevention of the abdominal compartment syndrome. J Traum 2003 47:509-13.
17. Karakozov, Michael: Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. 2002, Intensive Care Unit, Republican Hospital of Karelia Petrozavodsk, Russia.
18. Nathens Avery M, Frederick D, Brenneman M, Bernard R, Boulanger, M. The abdominal compartment syndrome. Canadian Journal of Surgery 2005; 40(4): 254.
19. Olivera Guzmán CI, Vázquez García MA, Martínez Sánchez J. et al. Efectos hemodinámicos y ventilatorios de la presión intraabdominal. Revista de la Asociación Mexicana de Medicina Critica y Terapia Intensiva. 2002; 14:3.
20. Safran DS, Orlando R. Physiologic effects of neumoperitoneum. Am J Surg 2004; 167:281- 6.
21. Kron IL, Harman PK, Nolan AP. The measurement of intraabdominal pressure as criterio for abdominal re-exploration. Ann Surg 2002; 199:28-30.
22. Rubinson RM, Vasco JS. Inferior cava obstruction for increased intraabdominal pressure. Arch Surg 2003; 94:760-6.
23. Cullen DJ, Coyle JP. Cardiovascular, renal and pulmonary effects of massively increased intraabdominal pressure in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 2004; 17: 119-21.
24. Benham J, Coetlee CJ, Papaglonopoulos C. Abdominal comparment syndrome. J Trauma 2003; 38: 152-3.
25. Gracias VH, Braslow B, Johnson J. et al. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in the Open Abdomen. Arch Surg 2002;137: 1298-1300.
26. Schein M, Wittman DH. The abdominal compartment syndrome following peritonitis, abdominal trauma and operations. Complicat Surg 1993; 15(5):745-53.
27. Turnbull D, Mills GH. Abdominal pressure in the prone position: implications for visceral perfusion. AORN J 2005; 69:560-7.
28. Bloomfield G, Saggi B, Blocher C, Sugerman H. Physiologic effects of externally applied continuous negative abdominal pressure for intra-abdominal hypertension. Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection and Critical Care. 2004; 46(6): 1014-6.
29. Bloomfield GL, Ridings PC, Blocher CR, Marmarou A, Sugerman HJ. A proposed relationship between increased intra-abdominal, intrathoracic, and intracranial pressure. Crit Care Med March 2005; 25(3):496-503.
30. Flores -Álvarez E, Ávila-Cuevas GE, De la Torre-González JL, Rivera-Barragán V, López-Rodríguez JL, Reynoso-Talamantes D. Detección temprana y factores de riesgo asociados al síndrome compartimental abdominal. Cirugía y cirujanos 2005; 73(3).
31. Rubio Silveira N,Canino Cereijo K, Echevarría del Risco C, García Paneca K. Valor predictivo de la presión intrabdominal en 50 pacientes operados de urgencia. Rev SILAC 2003; 7(2): 21-8.
32. Kodakat SK, Ginsburg R, Gopal PB, Rela M. A case of post-reperfusion syndrome following surgery for liver trauma. British Journal
33. Vegar-Brozovic V, Stoic-Brezak J. Pathophysiology of abdominal compartment syndrome. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:833–835.
34. Luis F, Sangosanya A, Kaplan LF. Abdominal compartment syndrome: Clinical aspects and monitoring. Crit Care Clin. 2007;23:415–433.
35. Offner Patrick J, Laurence de Souza A, Ernest E, Moore M. et al. Avoidance of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Damage-Control Laparotomy After Trauma. Arch Surg. 2003; 136: 676-81.
36. Barba CA. The intensive care unit as an operating room. Surg Clin North Am. 2003; 80 (3).
37. Carrasco JA. Patología colónica aguda en la unidad de cuidados intensivos. Medwave. Congreso de Medicina Intensiva de america del sur. Iquique 2002 Año 3, No. 8, Edición Septiembre 2003. Hospital Soco de la capital Federal de México.
38. Von Gruenigen VS, Coleman RL, King MR, Miller DS. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in gynecologic surgery. Obstet Gynecol 2003; 94 (5): 830-2.
39. Pearl LS, Trunkey DD. Compartment Syndrome of the liver. J Trauma 2005; 47 (4): 796-8.
40. Diebel LN, Dulchavsky SA, Brown WJ. Splanchnic ischemia and bacterial translocation in the abdominal compartment syndrome. J Trauma. 1997;43:852–855.
41. Sugrue M, Jones F, Lee A, y col.: Intraabdominal pressure and gastric intramucosal pH: is there an association? World J Surg 20:988-91, 1996.
42. Pickhardt PJ, Shimony JS, Heiken JP, Buchman TG, Fisher AJ.The abdominal compartment syndrome. CT findings. Am J Roentgenol 2003; 173(3): 575-9.
43. Ciresi DL, Cali AF, Senagore AJ: Abdominal closure using nonabsorbable mesh after massive resuscitation prevents abdominal compartment syndrome and gastrointestinal fistula. Am Surg 2002; 65 (6): 7220-4.
44. Watson RA, Novdieshell TR. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. South Med J 2003; 91 (4): 326-32.
45. Semb KA, Aamdal S, Fossa SD, Oian P. Transcapillary forces of the subcutaneous tissue in patients treated with interleukin-2 and alpha-interferon: on capillary protein leak syndrome? J Exp Ther Oncol 2005; 1 (3): 155-61.
46. Citerio G, Vascotto E, Villa F, Celotti S, Pesenti A. Induced abdominal compartment syndrome increases intracranial pressure in neurotrauma patients: A prospective study. Crit Car Med. 2000;29:1466–1471.
47. Reber PU, Patel AG, Toyama MT, Ashley SW, Reber HA. Feline model of chronic obstructive pancreatitis: effects os acute pancreatic duct decompression on blood flow and interstitial pH. Scand J Gastroenterol 2004; 34 (4): 439-44.
48. Loren Y. Intrabdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome in trauma; pathophysiology and interventions. AACN Clin Issues 2003; 10 (1):104-12.
49. Sherck J, Seiver A, Shatney C, Oakes D, Cobb L. Covering the "open abdomen": a better technique. Am Surg 2002; 64 (9):854-7.
50. Yol S, Kartal A, Tavli S, Tatkan Y. Is urinary bladder pressure a sensitive indicator of intra-abdominal pressure? Endoscopy. 2002; 30: 778-80.
51. Ivatury, RR; Diebel, L; Porter, LM; Simon, RJ. Intra-abdominal hypertension and the abdominal compartment syndrome. Surg Clin N Am 2005; 77(4):783-800.
|