|
Correlacion neuropsicologica entre enfermedad de Parkinson y Demencia de tipo Alzheimer .8
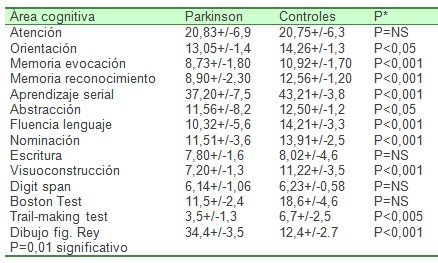
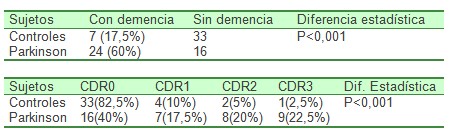
Tabla III-resultados de la evaluación neuropsicológica
Referencias:
1. Lees A, Smith E. Cognitive deficits in the early stages of Parkinson's disease. Brain 1983;106:257-270.
2.Elizan T,Sroka H,Maker H,Smith H & Yahr M.Dementia in idiophatic Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neural Transmission 1986;65:285-302.
3. PirozzoloF, Hansch C, Mortimer J.Dementia in Parkinson's disease: Neuropsychological analysis. Brainand Cognition 1982;1:71-83.
4. Lieberman A,Dziatolowsqui M,Kupersmith M, et al. Dementia in Parkinson's disease. Annals of Neurology 1979;6:355-359.
5. Mortimer J, Pirozzolo F, Hansch E & Webster D. Relationship of motor symptoms to intellectual deficits in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 1982;32:133-137.
6. Taylor AE,Saint-Cyr JA, Lang AE. Frontal lobe dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. The Cortical Focus of Neostriatal Outflow. Brain 1986; 109:845-883.
7. HornyKiewicz O y Kirsh S. Neurochemical basis of dementia in Parkinson's disease. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1984;11:185-190.
8. Delong MR, Georgopulos AP, Crutcher MD. Cortico-basal ganglia relations and coding of motor performance. In: neuralcoding of motor performance. Experimental Brain Research. Berlin:Springer 1983:30-40.
9. Selby G.Stereotactic surgery for the relief of Parkinson's disease. Part I. A critical review. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1967;5:315-342.
10.Johnston T,Rosvold H,Mishkin M. Proyectionsfrom behaviorally defined sectors of the prefrontal cortex to the basalganglia, septum and diencephalon of the monkeys. Experimental Neurology 1968;21:20-30.
11. Rosvold H. The frontal lobe system: cortical subcortical interrelationships. Acta neurobiological Experimentalis, Warsaw 1972;32:439-460.
12.Teuber H, Proctor F. Some effects of basal ganglia lesions in subhuman primates and man. Neuropsychologia 1964;2:85-93.
13.Johnston T, Rosvold H, Mishkin M. Proyections from behaviorally defined sectors of the prefrontal cortex to the basal ganglia,septum and diencephalon of the monkeys. Experimental Neurology 1968;21:20-30.
14.Cools A. Role of the neostriatal dopaminergic activity in sequencing and selecting behavioral strategies: Facilitation of processes involved in selecting the best strategy in a stressful situation. Bheavioral Brain Research 1980;1:361-378.
15. Divac I, Rosvold H, Szwarcbart M. Behavioral effects of selective abalation of the caudate nucleus. Journal of Comparative Physiology and Psychology 1967;63:184-190.
16. Taylor A, Saint-Cyr J, Lang, A. Parkinson's disease:Cognitive changes in relation to treatment response. Brain 1987;110:35-51.
17. Bowen F, Kamienny R, Burns M, Yahar M. Parkinsonism:Effects of levodopa treatment on concept formation.Neurology 1975;25:701-704.
18. Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y. Is the mesocortical dopaminergic system involved in Parkinson disease? Neurology 1980;30:1326-1330.
19. Uhl GR, Hedreen JC, Price DL. Parkinson's disease: Loss of neurons from the ventral tegmental area contralateral to therapeutic surgical lesions. Neurology 1985;35:1215-1218.
20. Scatton B, Rouquier L, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y. Dopamine deficiency in the cerebral cortex in Parkinson disease. Neurology 1982;32:1039-1040.
21. Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS. Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamina in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 1979;205:929-932.
22.Agid Y, Ruberg M, Dubois B, et al. Parkinson's disease and dementia. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1986;9:522-536.
23.Agid Y, Javoy-Agid, Ruberg M. Biochemistry of neurotransmitters in Parkinson's disease. In: Marsden CD, Fhan S, Eds. Movement Disorders 2. London Butterworths, 1987:166-230.
24. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington: American Psychiatric Association, 1980:205-224.
25.Cummings J. L. Subcortical Dementia Neuropsychology, Neuropsychiatry and Pathophysyology, British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;149:682-697.
26. Cummings J.L. & Benson D.F. Dementia: A clinical approach, Boston: Butterworths,2nd Edition, 1992
27. Cummings J.L., Benson D.F. Subcortical Dementia Review of an Emerging concept., Archives of Neurology 1984; 41:874-879.
28. Obler L, Albert M.Language and aging:A neurobehavioral analysis. En D.Beasley & G.Davis (eds), Aging:Communication Processes and Disorders, Grune &Stratton, New York, 1981,107-121.
29. Huber S, Shuttleworth E, & Freidenberg D. Neuropsychological differences between the dementias of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Archives of Neurology 46: 1287-1291, 1989.
30. Sullivan E, Sagar H, Gabrieli J, Corkin S & Growdon J. Different cognitive profiles on standard behavioral tests in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 1989; 11:799-820.
31. Garron D, Klawans H, & Narin F. Intellectual functioning of persons with idiopathic parkinsonism. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disorders 1972; 154:445-452.
32. Birkmayer W, Reiderer P, Youdin M. Distinction between benign and malignnant type of Parkinson's disease. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 1979; 81:158-164.
33. Martilla R, & RinneU. Dementia in Parkinson's disease.Acta Neurologica Scandinava 1976; 54:431-441.
34. Litcher D, Corbett A, Fitzgibbon G, et. al.Cognitive and motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Archives of Neurology 1988;45: 854-860.
35. Dubois B. Neuronal basis of cognitive changes in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology 1989;11:969.
36. Portin R, & Rinne U. The effect of deprenyl on cognition and emotion in parkinsonian patients undergoing long term levodopa treatment. Acta Neurologica Scandinava 1983; Supplemen 135:135-144.
37. Bowen F, Brady E, & Yahr M. Short and long range studies of memory, intelligence and perception in Parkinson's patients treated with levodopa. En Siegfried (ed.), Parkinson's disease: Rigidity, Akinesia, and Behavior. Hans Huber, Bern 1973;315-318.
38. Huber S,Shuttleworth E, & Paulson G. Dementia in Parkinson's disease. Archives of Neurology 1986; 43: 987-990.
39. Boller F, Passafiume D, Keefe NC, Rogers K, Morrow L,& Kim Y. Visuospatial impairment in Parkinson's disease. Archives of Neurology 1980;41:485-490.
40. Hakim A & Mathieson G. Dementia in Parkinson's disease: A neuropathological study.Neurology 1979;29:1209-1214.
41. Leverenz J & Sumi M. Parkinson's disease in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Archives of Neurology 1986;43:662-664.
42. De la Monte S, Wells S. Hedley E, & Growdon J.Neuropathological distinction between Parkinson's dementia and Parkinson's plus Alzheimer disease. Annals of Neurology 1989; 26:309-320.
43. Heilg C, Knopman D, Mastri A & Frei D.Dementia without Alzheimer pathology. Neurology 1985; 43:762-765.
44. Brook D, & Frackowiak R. PET and movement disorders. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1989; Special Supplement:68-77.
45. Zetusky W, Jankovic J,Pirozzolo F. The heterogeneity of Parkinson's disease: clinical and prognostic impilications.Neurologyy 1985;35:522-526.
46. Raskin S, Borod J, Tweedy J. Neuropsychological Aspects of Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychology Review 1990; 1:185-221.
|