Figura IV: Imágenes por Resonancia Magnética de arteria coronaria aterosclerótica de conejo y de muestras histopatológicas
Fuente: Sharma and Singh. Thrombosis Journal 2004; 2:5
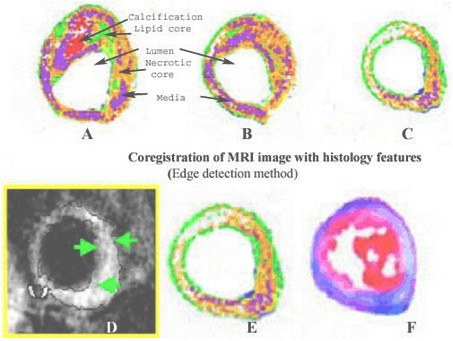
Different artery atheroma features are represented on coronary artery postsegmented feature map images for distinct plaque components and media layer (first and second panels on top). The combinations of different signal intensities (panels A-F) predict the distinct color-coded plaque feature(s) by using robust VTK program. At bottom, a proton density in vivo MRI image (left panel) shows dark areas of fibrous layer (arrow), lipid rich regions (gray areas open arrow). T2 parametric in vivo image (left panel) is shown with corresponding postsegmented image (middle panel) with corresponding coronary artery histology section showing different areas corresponding with varying T2 ranges for different atheroma components shown in Table 6. On histology sections, matrix appears bluish, calcification show gaps, atheroma as red and continuous fibrous layer.
Figura V: Imágenes arteria coronaria aterosclerótica de conejo
Fuente: Sharma and Singh.Thrombosis Journal 2004; 2:5
Referencias
1. Aguilera C, Mesa M, Ramírez-Tortosa M, Quiles J, Gil A. Virgin olive and fish oils enhance the hepatic antioxidant defence system in atherosclerotic rabbits. Clinical Nutrition 2003; 22(4):379-384
2. Alarcón M, Añez N, Calderón L, Matousek A. Evaluación de la ingesta de colesterol en conejos infectados con Tripanosoma cruzi. Kasmera 2004; 32(2):117-126
3. Alfonso M, Almeida G, Quintela A, Carballo R. Evaluación de un posible modelo experimental de aterosclerosis carotídea en conejos hipercolesterolémicos. Rev Cubana Invest Biomed 2001; 20(3):192-196
4. Alfonso Pérez C, Ortiz H. The relationship between the degree of dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia in the rabbit and atherosclerotic lesion formation. Atherosclerosis 2001; 102:9-22
5. Amran A, Zakaria Z, Othman F, Das S, Raj S, Nordin M. Aqueous extract of Piper sarmentosum decreases atherosclerotic lesions in high cholesterolemic experimental rabbits. Lipids in Health and Disease 2010; 9(1):44
6. Araujo J, Romano E, Brito B, Parthé V, Romano M, Bracho M. Iron overload augments the development of atherosclerotic lesions in rabbits. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995; 15:1172-1180
7. Aster M, Scorza T, Gallardo L, Hamana N. Alteraciones bioquímicas en conejos alimentados con aceite de palma y maíz y su relación con los hallazgos morfológicos. Revista de la Facultad de Medicina 2004; 27(1)
8. Belland R, Ouellette S, Gleffers J, Byrne G. Chlamydia pneumoniae and atherosclerosis. Cellular Microbiology 2004; 6(2):117-127
9. Bleys J, Miller E, Pastor-Barriuso R, Appel L, Guallar E. Vitamin-mineral supplementation and the progression of atherosclerosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006; 84:880-887
10. Bocan T, Mueller S, Mazur M, Uhlendorf P, Brown E, Kieft K. Efectos del aceite crudo de palma en los lípidos plasmáticos de conejos. Revista de la Facultad de Medicina 1993; 24(1)
11. Bosze Z, Hiripi L, Carnwath J, Niemmann H. The transgenic rabbit as model for human diseases and as a source of biologically active recombinant proteins. Transgenic Research 2003; 12:541-553
12. Cabré A, Girona J, Vallvé J, Masana L. Aldehydes mediate tissue factor induction: A possible mechanism linking lipid peroxidation to thrombotic events. Journal of Cellular Physiology 2003; 198(2): 230-236
13. Camera M, Vincenzo T, Comparato C, Baetta R, Rossi F, Fuortes M, Ezekowitz M, Paoletti R, Tremoli E. Cholesterol-induced thrombogenicity of the vessel wall: Inhibitory effect of fluvastatin. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 2002; 87(4):748-755
14. Caron M, White M. Evaluation of the antihyperlipidemic properties of dietary supplements. Pharmacotherapy 2001; 21(4)
15. Castelo-Branco C, Sanjuán A, Ascaso C, Colodrón M, Blϋmel J, Casals E, Ordi J, Vanrell J. Tibolone inhibits aortic atherosclerotic lesion formation in oophorectomized cholesterol-fed rabbits. Experimental Clinical Cardiology 2003; 8(1):21-25
16. Cavallini D, Abdalla D, Vendramini R, Bedani R, Bomdespacho L, Pauly-Silveira N, Valdez G, Rossi E. Effects of isoflavone-supplemented soy yogurt on lipid parameters and atherosclerosis development in hypercholesterolemic rabbits: a randomized double-blind study. Lipids in Health and Disease 2009; 8:40
17. Cheong S, Kim M, Sok D, Hwang S, Kim J, Kim H, Lee J, Kim Y. Spirulina prevents atherosclerosis by reducing hypercholesterolemia in rabbits fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 2010; 56:34-40
18. Cottrell R. Introduction: nutritional aspects of palm oil. J Clin Nutr 1991; (53):989S-100S
19. Dabbagh A, Shwaery G, Keaney J, Frei B. Effect of iron overload and iron deficiency on atherosclerosis in the hypercholesterolemic rabbit. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 1997; 17:2638-2645
20. Dalloz F, Osinka H, Robbins J. Genetically modified animal models in cardiovascular research. Revista Española de Cardiología 2001; 54(6): 764-789
21. de Castro M, Veiga A, Pacheco M. Plasma lipid profile of experimentally induced hyperlipidemic New Zealand white rabbits is not affected by resveratrol. The Journal of Applied Research 2009; 9(1):18-22
22. de La Cruz J, Villalobos M, Carmona J, Martín-Romero M, Smith-Agreda J, de la Cuesta F. Antithrombotic potential of olive oil administration in rabbits with elevated cholesterol. Thrombosis Research 2000; 100(4):305-315
23. Draper H, McGirr L, Haldey M. The metabolism of malondialdehyde. Lipids 1986; 21:305-307
24. Flores-Pérez F, Pérez-Martínez M. Avances en el estudio de la fisiología y patología endotelial en modelos animales. Vet. Méx. 2006; 37(2):239-261
25. Fong I, Chiu B, Viira E, Fong M, Jang D, Mahoney J. Rabbit model for Chlamydia pneumoniae infection. J Clin Microbiol 1997; 35:48-52
26. Fox R. Taxonomy and genetics. En: The Biology of the Laboratory Rabbit. (Weisbroth S, Flatt R and Kraus A, eds.) Academic Press, San Diego, 1974, pp. 1-22
27. Gapor A, Berger K, Hashimoto T et al. Effects of processing on the content and composition of tocopherols and tocotrienols in palm oil. In: Pushparajah E, Rajadurai M, eds. The palm oil product technology in the eighties. Kuala Lumpur: Incorporated Society of planters 1983:145-156
28. Gersh B, Sliwa K, Mayosi B, Yusuf S. Novel therapeutic concepts: the epidemic of cardiovascular disease in the developing world: global implications. European Heart Journal 2010; 31(6):642-648
29. Gil A, Ramírez M, Aguilera M, Mesa M. Modelos experimentales de enfermedad cardiovascular. Nutrición Hospitalaria 2007; 22(2):169-177
30. Halliwell B, Gutteridge J. Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage and antioxidant therapy. Lancet 1984; 1:1396-1397
31. Harkness J, Wagner J. Biología y clínica de conejos y roedores.1980. Editorial Acribia