|
Caracterizacion de los pacientes con Enfermedad Cerebrovascular .14
8- Acciones Independientes de Enfermería realizadas:
___Vigilancia estado conciencia
___ Valoración del lenguaje
___ Valoración orientación
___ Posición decúbito supino con ángulo favorable para oxigenación cerebral
___ Cuidados paciente comatoso
___ Alimentación artificial
___ Ejercicios pasivos en el lecho
___ Fisioterapia postural
___ Control Hidromineral
___ Vigilancia complicaciones
___ Restricción en el lecho
___ Otras ¿Cuál? _____________________________________
Anexo Nº 2
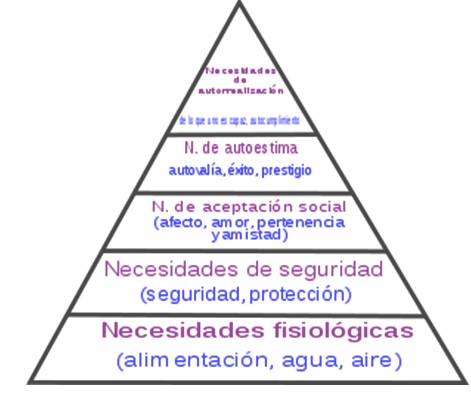
Jerarquía de las necesidades de Maslow, utilizada para priorizar los problemas de salud encontrados en el paciente.
REFERENCIAS BIBLIOGRÁFICAS
1- Organización Panamericana de Salud. La Salud en las América. Publicación científica-técnica 2004; 587(2): 203-10
2- Smith SW, Hauser LS, Donald J: Enfermedades Cerebrovasculares. En: Braunwald E, Fauci SA, Kasper LD, Hauser LS, Longo LD, Larry J: Harrison. Principios de Medicina Interna. 15ª ed. México: McGraw- Hill Interamericana; 2002: 2769-97(3).
3- Ruiz D: Enfermedad Cerebrovascular. En: Rodríguez MH, Pérez DM, Torres W, Carnot J, Pardo A, Páez AI: Manual de Diagnóstico y Tratamiento en Especialidades Clínicas. 1raed. La Habana: Política; 2002:260-3(10).
4- Gómez N, Rivera E: Características Clínicas e Imagenológicas de la Demencia Vascular. RevCubana. Med. 1998; 37(1):6-12(22).
5- Turrent J, Talledo L, González A, Gundían J, Remuñán C: Comportamiento y Manejo de la Enfermedad Cerebrovascular en una Unidad de cuidados Intensivos. Revista Cubana de Medicina Intensiva y Emergencias 2004: http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/med.(4).12-20.
6- Kondo R, Matsumori Y, Kato N, Tsuchiya D, Kokubo Y, Sato S, et al: Trends in the Incidente of Stroke in Yamagata, Japan. No To Shinkei 2006; 58(3):213-8.
7- Fernández O, Pando A, Buergo AM, Mestre R, Moreno J: Enfermedad Cerebrovascular. En: Álvares R, Díaz G, Salas I, Rosa E, Batista R, autores: Temas de Medicina General Integral. 1ra ed. La Habana: Ecmed; 2001: 895- 910 (1).
8- Fernández O, Pando A, Buergo AM, Mestre R, Moreno J: Enfermedad Cerebrovascular. En: Álvares R, Díaz G, Salas I, Rosa E, Batista R, autores: Temas de Medicina General Integral. 1ra ed. La Habana: Ecmed; 2001: 895-910.
9- Smith SW, Hauser LS, Donald J: Enfermedades Cerebrovasculares. En: Braunwald E, Fauci SA, Kasper LD, Hauser LS, Longo LD, Larry J: Harrison. Principios de Medicina Interna. 15ª ed. México: McGraw- Hill Interamericana;2002:2769-97.
10- Turrent J, Talledo L, González A, Gundían J, Remuñán C: Comportamiento y Manejo de la Enfermedad Cerebrovascular en una Unidad de cuidados Intensivos. Revista Cubana de Medicina Intensiva y Emergencias2004:http://bvs.sld.cu/revistas/med.
11- Abel I, Verhey F: Depression after a Cerebrovascular Accident. The Importance of the Integration of Neurobiological and Psychosocial Pathogenic Models. Panminerva Med 2006; 48 (1): 49- 57.
12- Johnston CS: Transient Ischemic Attack. N Engl J Med 2002; 347 (21): 1687-92.
13- Albers WG, Caplan RL, Donals J, Fayad BP, Mohr PJ, Saver LJ, et al: Transient Ischemic Attack- Proposal for a New Definition. N Engl J Med 2002;347(21): 1713-16.
14- The National Institute of Nuerological Disorders and Stroke: Procedings of a National Symposium on Rapid Identification and Treatment of Acute Stroke.Dec.12-13, 1996.
15- Ruiz D: Enfermedad Cerebrovascular. En: Rodríguez MH, Pérez DM, Torres W, Carnot J, Pardo A, Páez AI: Manual de Diagnóstico y Tratamiento en Especialidades Clínicas. 1ra ed. La Habana: Política; 2002: 260- 3.
16- Broderick JP: Heart Disease and Stroke. Heart Dis Stroke 1993; 2 (4): 355- 9.
17- Ikeda T, Gomi T, Kobayashi S, Tsuchiya H: Role of Hypertension in Asumptomatic Cerebral Lacunae in the Elderly. Hypertension 1994; 23 (Suppl1):1259-62.
18- Pérz J, Beguería R: Recurrencias en el Infarto cerebral. Rev. Cubana Med1996; 35(1).
19- Basu AK, Pal SK, Saha S, Bandyopadhyay R, Mukherjee SC, Sarkar P: Risk Factor Analysis in Ischaemic Stroke: a hospital- based study. J Indian MedAssoc2005;103(11):586-8.
20- Fujishima M, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, Ohmura T, Iwamoto H, Nakayama K, et al: Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease in a Prospective Population Survey in Japan: the Hisayama study. Diabetes 1996; 45 (Suppl 3): 14- 6.
21- Sandercock P, Bamford J, Dennis M, Burn J, Slattery J, Jones L, et al: Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke: prevalence in different types of stroke and influence on early and long term prognosis. BMJ 1992; 305 (68); 1460- 5.
22- Sokol SI, Kapoor JR, Foody JM: Blood Pressure Reduction in the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Stroke. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2006; 4 (2):155-60.
23- Alvárez Sabin, A. Caracterización del Ictus en pacientes de Riesgos. Enfermería y Ciencias. 5ta Ed. Ediciones Harcourt España, 2002.
24- Giroud M, Dumas R: Rolé du Tabac Dans les Accidents Vasculaires Cérébraux. PresseMed1994;23(22):1037-9.
25- Gómez N, Rivera E: Características Clínicas e Imagenológicas de la Demencia Vascular. Rev Cubana Med 1998; 37 (1): 6- 12.
26-Alaranta, H., H. Hurri, M. Heliovaara, A. Soukka, And R. Harju. Non-dynamometric trunk performance tests: Reliability and normative data. Scand. J. Rehabil. Med. 26:211–215. 1994.
27-. Alaranta, H., S. Luoto, M. Heliovaara, and H. Hurri. Static back endurance and the risk of low-back pain. Clin. Biomech. 10:323–324. 1995.
28-. Alexander, M.J. Biomechanical aspects of lumbar spine injuries in athletes: A review. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 10:1–20. 1995.
29- Bergmark, A. Stability of the lumbar spine. A study in mechanical engineering. Acta. Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 230:S20–S24. 1989.
30- Biereng-Sorenson, F. Physical measurements as risk factors for low-back trouble over a one year period. Spine. 9:106–119. 1984.
31-. Bono, C.M. Low-back pain in athletes. J. Bone Joint. Surg. Am. 86:382– 396. 2004.
32-. Carpenter, D.M., and B.W. Nelson. Low back strengthening for the prevention and treatment of low back pain. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 31:18–24. 1999.
33-Whitfield PC; Moss H: An audit of aneurismal subdarachoid haemorrage: earlier ressuscitation and surgery reduces inpatient stay and deaths. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60: 301-306, 1996.
34- Gibbs SR: Timing of aneurysm surgery. En: Bradley WC: Year Book of Neurology and Neurosurgery; pag. 230. Mosby Inc. St. Louis, 1998.
35- Yund KD, Dacey RG: Hospital resource in the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 85: 403-409, 1996.
36- Bondurant CP: Nontraumatic SAH; complications and cost. En: Bradley WC: Year Book of Neurology and Neurosurgery; pag. 223. Mosby Inc. St. Louis, 1998.
37- Ponte, C y colaboradoes. Accidentes vasculares encefálicos en regiones venezolanas. www.acv.cantv.net
38- Elliott JP: Predicting lengh of hospital stay and cost by aneurism grade on admission. J Neurosurg 85: 388-391, 1996.
39- Leblanc R: Familial cerebral aneurysms: A bias for women. Stroke 27: 1050-1054, 1996.
40- Schievink WI: Alpha – 1 – antitrypsin phenotypes among patients with intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 84: 781-784, 1996
41- Lindquist C, Wikholm G: Embolization of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 39: 460-469, 1996.
42- Bembibre R, Soto A, Díaz D, Hernández A. Epidemiología de Enfermedad Cerebrovascular hemorrágicos en la región central de Cuba. Rev. Neurol. 2004;33(7): 601-4.
43- Pérez Romero GE. Enfermedad Cerebrovascular en Calí, Colombia. Acta Neurol Coloma. 2004; 20(3): 97-8
44- Roca Goderich R. AVE. Temas de Medicina Interna. Tomo 2. La Habana. Editorial Pueblo y Educación 2003; 587(2): 203-9.
45- Clarke K. Emergency Medicine. 3ed. 2002.
46- Gurmary Escalona B, Dejar de fumar y disminuir el riesgo AVE. Rev. Cub. MGI 2003:95.
47- Rabos A, Vail Llosera A, García Eroles G. Clinical factures and functional outcomo of intracerebral hemorrhage in patients age 85 and older. J Am Geriatría 2004; 50:449-53.
49- Naranjo Y, Bermúdez. Mortalidad por enfermedad cerebrovascular en Guanabacoa, Cuba. Rev. Neurol.2004; 30(9) 898-9.
50- Bembibre R, Poma D, Hernández A. AVE Hemorrágico. Estudio multicentrico en 3 años en la región central de Cuba. Rev. Española Neurol 2004; 33(7): 1234-8.
51- J.J. Sánchez Chávez. Etiología de las enfermedades cerebrovasculares Simposio internacional Avances recientes en Neurología. Curso postevento. Enfermedad cerebro vasculares. Ciudad Habana.1998.
52- Luciñaga, M; Diez Tejedor, E: “Guía para el manejo del paciente con enfermedad cerebro vascular aguda”, Rev. Neurol. (Barc), 1995:23:363-9.
|